|
Currently no newer database. Click here to access existing scholarly databases.
|
|
|
|
3.3 How do I construct an Advanced Search?
You may search by Anywhere, Author, Title, Subject and ISBN. It looks for an exact match, so spelling is important.
In Advanced Search, you may search by :
| Field | Returned items |
| Anywhere | With the words appearing anywhere |
| Title | With the words in the title |
| Author | By author |
| Subject | In this subject area |
| ISBN Number | Associated with the designated number |
| | |
Anywhere
An anywhere search uses one or more complete words (keywords) in a search. Keywords may appear anywhere in the record, including titles, notes, abstracts, summaries, descriptions and subjects. The keywords can also be names of people and places that are the subjects of a library resource or a listing in a directory.
| | |
| Type key search terms in at least one field - Advanced Search
|
| |
3.3.1 Tips for constructing searches
In keywords searching, you can specify left, right or medial truncation and wild card searches.
- Example : Use an asterisk (*) to designate one ore more characters:
Mar* will retrieve market, marketing, marketplace, margin, marathon, etc.
St*s will retrieve statistics, states, statements, etc.
- Example : Use of question mark (?) to designate a single character. Use two question marks to designate two characters, and so forth:
Ho? will retrieve hop, hog, hot, etc
Wa?n will retrieve warn
w??en will retrieve women, woven, wooden, etc.
|
| |
3.3.2 Using Boolean searches
Boolean searches let you broaden or narrow searches. The three Boolean search operations the catagloue supports are:
- AND (to narrow your search)
- OR (to broaden your search)
- NOT (to narrow your search by exclusion of a search term)
| | |
Boolean operators allow you to have greater control over the way you search :
- OR
By using the Boolean operator OR you can combine multiple terms into one search to find more records. OR is most helpful for broad searches for similar terms.
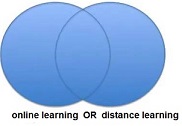
For instance, a search for online learning or distance learning will retrieve records in which at least one of the search terms is present.
The shaded circle with the word online learning represents all the records that contain the word online learning
The shaded circle with the word distance learning represents all the records that contain the word distance learning.
The shaded overlap area represents all the records that contain both online learning and distance learning.
- AND
By using the Boolean AND you can combine your search terms to try and limit the amount of records you get or to make them more specific to your search. An AND search will only return records with all your search terms in them.
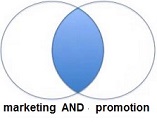
A search for marketing and promotion will retrieve records in which BOTH of the search terms are present.
The shaded area represents all the records that contain both the word marketing and promotion.
- NOT
By using the Boolean NOT you can combine your search terms so try and limit the amount of material or "hits" you get, or to eliminate irrelevant terms. A NOT search will only return records that do hot have specified terms.
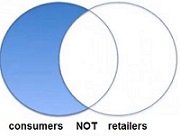
The NOT operator is used to reduce the number of hits you get. For instance, a search for consumers NOT retailers will retrieve records in which only one of the words is present.
The shaded area with the word consumers represents all the records that contain the word consumers.
No records are retrieved in which the word retailers is present, even if the word consumers appears there too. Use with care as you may be eliminating useful records.
|
| |
| |
| |
| Back | |
| |
| Step 1: | Develop your topic |
| Step 2: | Find background information |
| Step 3: | Use the Library catalogue |
| Step 4: | Search MyDigital Library |
| Step 5: | Find information on the World Wide Web (WWW) |
| Step 6: | Review and evaluate your sources |
| Step 7: | Cite your resources using a standard format |
|
|
|
|